Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that
best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
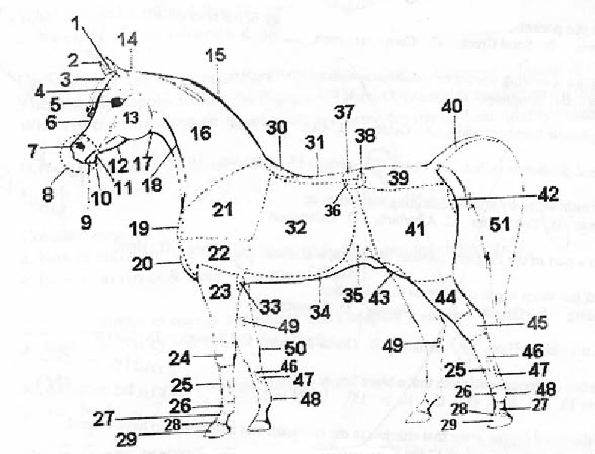
Number 25 on the above diagram isa. | pastern | b. | hoof | c. | cannon bone | d. | hock |
|
|
|
2.
|
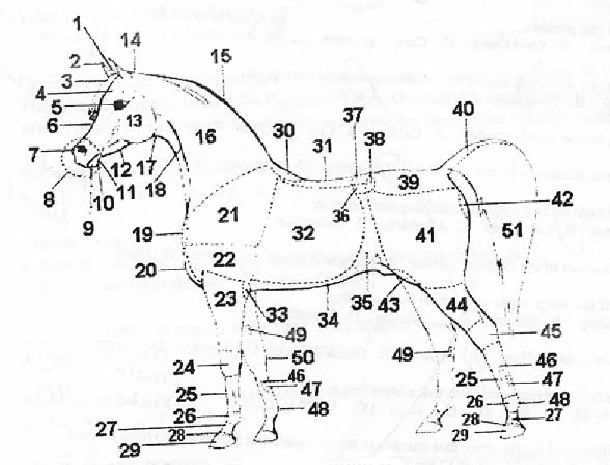
Number 45 on the above diagram isa. | hock | b. | knee | c. | pastern | d. | hoof |
|
|
|
3.
|
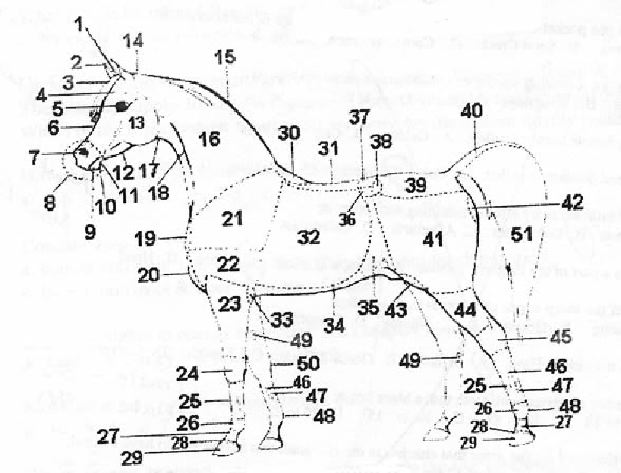
Number 8
on the above diagram isa. | nostril | b. | muzzle | c. | nose | d. | chin |
|
|
|
4.
|
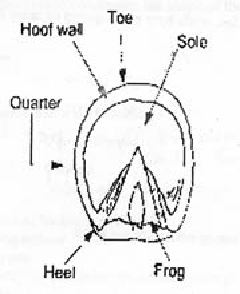
The above
picture isa. | the
hoof | c. | the dissection of the cannon
bone | b. | the underside of the hoof | d. | none of these are correct |
|
|
|
5.
|
A horse weighing around 1000
lbs. voids how many quarts of urine daily?
a. | 1 1/2 to 8 1/2
quarts | c. | 5
gallons | b. | 10 gallons | d. | 2 quarts |
|
|
|
6.
|
A horse’s heart weighs
about
a. | 4
pounds | b. | 10
pounds | c. | 2
pounds | d. | 20
pounds |
|
|
|
7.
|
Horses knee caps are not done
fusing until they are about
a. | 1 year
old | c. | 3 years
old | b. | 1-1/2 years old | d. | 3-1/2 year old |
|
|
|
8.
|
Horses hooves grow at a rate of
about
a. | 2 cm per
month | c. | 3 cm per
month | b. | 1 cm per month | d. | 10 mm per month |
|
|
|
9.
|
Horses have about how many
bones in their body?
|
|
|
10.
|
A habit including kicking,
bucking, biting and striking is commonly referred to as a
a. | vice | c. | Splashonanism | b. | agnostic behavior | d. | ADHD |
|
|
|
11.
|
Around 9 or 10 years of age a
longitudinal depression manifests upon the upper corner incisor this is called
the?
a. | cup | c. | Galvaynes groove | b. | dental star | d. | bowl |
|
|
|
12.
|
The filing of sharp edges of a
horse’s teeth is termed
a. | stripping | b. | gnawing | c. | floating | d. | leveling |
|
|
|
13.
|
This skeletal protrusion
constitutes the slope of the foot and stiffness to bear weight.
a. | sole | b. | hammer | c. | coffin bone | d. | ingrown hoof |
|
|
|
14.
|
What are the symptoms of a mare
foaling?
a. | cribbing | b. | waxing | c. | sweating | d. | biting |
|
|
|
15.
|
This action induces
barker’s syndrome
a. | foals nursing
refusal | b. | lack of oxygen | c. | the mares individual antibodies created during
gestation | d. | moldy hay |
|
|
|
16.
|
By using the hormone _________
ovulation can be commenced at will.
a. | GNrH | c. | Acetaminophen | b. | Lutalyse | d. | BhT |
|
|
|
17.
|
Strangles is dangerous to
humans and small rodents.
|
|
|
18.
|
The hoof shell is called the
a. | enamel | b. | periople | c. | stifle | d. | casing |
|
|
|
19.
|
Vitamin D daily requirements
can be acquired with ________ of sunlight.
a. | 1 hour | b. | none | c. | 30 minutes | d. | 24 hours |
|
|
|
20.
|
A horse’s stifle is
similar to what joint in the human body?
a. | shoulder | b. | knee | c. | hip | d. | elbow |
|
|
|
21.
|
Carbohydrates are most
prevalent in what type of feed?
a. | Omolene | b. | 911 | c. | corn | d. | alfalfa |
|
|
|
22.
|
This tool is implemented for
the removal of excrement from hoofs.
a. | hoof
pick | c. | hand mini
shovel | b. | dung destroyer | d. | tooth pick |
|
|
|
23.
|
60 inches would be how many
hands?
|
|
|
24.
|
A star marking resides on this
part of a horse?
a. | between the
eyes | c. | buttocks | b. | nose | d. | neck |
|
|
|
25.
|
Name the color that is not a
base color.
a. | bay | b. | brown | c. | chestnut | d. | cremello |
|
|
|
26.
|
A _____________________ tends
to the care of a horses hoofs?
a. | veterinarian | b. | farrier | c. | podiatrist | d. | doctor |
|
|
|
27.
|
A dominant gene suppresses this
type of gene?
a. | dominant | b. | compulsive | c. | recessive | d. | introvert |
|
|
|
28.
|
A cross between a liver
chestnut and a black horse results in what color offspring?
a. | jet
black | b. | fading
black | c. | tobiano | d. | sabino |
|
|
|
29.
|
What piece of equipment is
vital to controlling a stud?
a. | gut
wrench | c. | stud
chain | b. | lip immobilizer | d. | balling gun |
|
|
|
30.
|
The main characteristic of a
mealy mouthed horse is that
a. | the mouth is
elongated | c. | the horse has an
irregular appetite | b. | the hair around the mouth is faded | d. | the horse is obese |
|
|
|
31.
|
This type of horse is athletic,
large and perfect for cross-country and jumping.
a. | stock | b. | plantation | c. | pleasure | d. | hunter |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which is not an essential for
proper horse feeding?
a. | water | c. | vitamins | b. | proteins | d. | none of these are correct |
|
|
|
33.
|
How many permanent teeth does
an adult female horse have?
|
|
|
34.
|
A male horse is called a colt
until what age?
|
|
|
35.
|
A monkey mouth is opposite of
what abnormality?
a. | parrot
mouth | b. | mealy
mouth | c. | grin | d. | overbite |
|
|
|
36.
|
A _________ contains the
cellular composition of an organism.
a. | chromosome | b. | allele | c. | Genome | d. | phenotype |
|
|
|
37.
|
During foaling a mare’s
inability to push a foal out of the birth canal is named?
a. | give | c. | foaling retardation | b. | labor fatigue | d. | dystocia |
|
|
|
38.
|
Tobiano coloring is dominated
by which color?
a. | brown | b. | white | c. | bay | d. | yellow |
|
|
|
39.
|
A common disease of horses
often called lockjaw is medically called?
a. | tetanus | b. | botulism | c. | hydrophobia | d. | myositis |
|
|
|
40.
|
Horses have two blind spots,
they are
a. | in front and
behind | c. | in front and
sides | b. | behind and sides | d. | behind and sides |
|
|
|
41.
|
A cold-blooded horse has this
type of temperament.
a. | angry | b. | placid | c. | anxious | d. | timid |
|
|
|
42.
|
Hinny is another word for what
type of animal?
a. | camel | b. | horse | c. | donkey | d. | mule |
|
|
|
43.
|
A face fly feeds on
what?
a. | secretions from the
eyes | c. | blood | b. | excrements | d. | saliva |
|
|
|
44.
|
Allelominetic behavior is
the
a. | copying of other horses at a young
age | b. | attention seeking horses | c. | pawing at the ground and rapid muscle
contraction | d. | mutual mimicking behavior |
|
|
|
45.
|
This type of saddle is best
used for roping and cutting.
a. | hunter | b. | gaited | c. | stock | d. | dressage |
|
|
|
46.
|
Phenotype is opposite
from
a. | manotype
| b. | DNA | c. | Heterozygous | d. | Genotype |
|
|
|
47.
|
This type of horse is a
breed.
a. | morab | b. | bay | c. | palomino | d. | roan |
|
|
|
48.
|
The best nutritional legume for
horses is?
a. | clover | b. | alfalfa | c. | bromegrass | d. | silage |
|
|
|
49.
|
This disease is similar to
asthma in humans.
a. | encephalitis | c. | heaves | b. | plueropneumonia | d. | strangles |
|